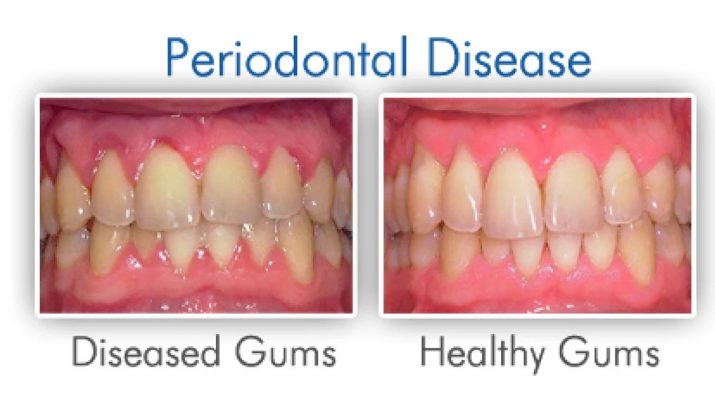
We pay extra attention and care to the other aspects of our body but often tend to neglect our oral health. This is when oral issues, such as gingivitis and periodontitis, begin surfacing. Periodontal diseases affect about 30-50% of the worldwide population.
Are your teeth appearing longer than usual? Try shaking them slightly with your fingers. Do they feel like they will fall off any moment? You could be suffering from periodontitis and need to visit a dentist immediately! To know more about this oral problem and how it can be treated, keep reading.
What Is Periodontitis?
Periodontitis (or gum disease) is a serious infection of the gums that can damage the soft tissues and bone supporting your teeth. If left untreated, this condition can cause the alveolar bone around the teeth to deteriorate completely. This can cause your teeth to loosen and may even result in some of them falling off.
Although periodontitis is quite common, it is largely preventable.
Periodontitis is usually the second stage of gum disease. Periodontal or gum disease is usually classified into three stages.
What Are The Stages Of Periodontal Disease?
The three main stages of the periodontal disease include:
- Stage 1 – Gingivitis
This is the most common stage of the disease. It results in the build-up of plaque around your gums and can cause inflammation, swelling, and even bleeding in some cases.
- Stage 2 – Periodontitis
If gingivitis is left untreated, it can turn severe, causing periodontitis. This infection goes on to threaten the gums, jawbone, as well as the surrounding bone.
- Stage 3 – Advanced Periodontitis or Periodontal Disease
When periodontitis advances to this stage, you are at high risk of losing some of your teeth as well as the bones and fibers that support them. This is the most severe stage that may result in persistent bad breath, toothaches, tooth loss, bone loss, etc.
In this article, we are dealing with the second stage of gum disease – periodontitis. Let’s now take a look at the signs and symptoms.
Signs And Symptoms
The common symptoms associated with periodontitis are:
- Inflamed, puffy, or swollen gums
- Gums may be bright red or purplish
- Tender gums that may bleed easily
- Receding gums that can make your teeth appear longer
- Increasing space between developing teeth
- Pus between the teeth and gums
- Loosening of your teeth
- Bad breath
- Toothache, especially while chewing food
What factors trigger periodontitis? Let’s find out.
What Causes Periodontitis Disease?
Most cases of periodontitis begin with the formation of plaques on your teeth and gums. Plaque formation can further contribute to the development of periodontitis via the following phases:
- The starches and sugars in the food you eat interact with the naturally occurring bacteria in your mouth. This leads to the formation of plaque on your teeth.
- When plaque is left unattended, it can cause your gum line to harden into tartar. Tartar is harder to get rid of, and you can’t remove it by simply brushing or flossing. You will have to visit a dentist to get rid of it.
- Untreated plaque and tartar lead to gingivitis. This is the beginning of periodontal disease that can cause irritation and inflammation in some part of your gums surrounding the base of your teeth.
- If gingivitis is left unattended, it leads to periodontitis, which causes pockets to develop in between your teeth and gums. These pockets are often filled with plaque, tartar, and bacteria.
The following are some common factors that can increase your risk of developing periodontitis.
Risk Factors
The most common risk factors for periodontitis include:
- Poor oral hygiene
- Gingivitis
- Chewing or smoking tobacco
- Hormonal changes or imbalances triggered by pregnancy or menopause
- Substance abuse
- Being obese
- Genetics – A family history of the condition
- Nutrition deficiencies – like that of vitamin C
- Certain medicational drugs that cause changes in your gums or make your mouth increasingly dry
- Medical conditions like leukemia and HIV/AIDS that cause your immunity to decline
- Other diseases like diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, or Crohn’s disease
- Cancer treatments like radiation therapy or chemotherapy
Many people confuse periodontitis for gingivitis due to the similarities in their symptoms. However, you must know that periodontitis is an advanced stage of gingivitis. The following are some of the major differences between the two.
Gingivitis Vs. Periodontitis
Some of the main differences between gingivitis and periodontitis are:
Gingivitis
- Gingivitis precedes periodontitis.
- Not all gingivitis cases progress to periodontitis.
- It is a result of plaque build-up on your teeth.
- Gums become inflamed and may even bleed due to gingivitis.
- The teeth remain firmly planted to your gums if you are suffering from gingivitis.
Periodontitis
- Some cases of untreated gingivitis advance to periodontitis.
- Periodontitis usually follows gingivitis.
- The inner layer of the gum and the bone pull away from your teeth, resulting in pockets between your teeth and gums.
- Your teeth may begin to loosen.
- Some of your teeth may also fall off.
When it comes to your oral health, it is best to avail of medical intervention immediately to prevent periodontitis from progressing any further.
When To See A Dentist
It is best to see a dentist immediately if you notice that gingivitis is recurring in your case. Get your teeth checked regularly or as advised by your dentist. The sooner you begin treatment, the better are the chances of reversing the damage before it turns permanent.
Once you visit a dentist, they might carry out the following tests to determine whether you are suffering from periodontitis or not.
How To Diagnosis Periodontitis
Your dentist may first begin by reviewing your medical history and lifestyle to identify any factors that could be contributing to the development of periodontitis.
Your dentist may:
- Examine your mouth to look for symptoms of the condition.
- Measure the depth of the pockets or holes that have formed due to the condition. The pockets of a healthy mouth are usually 1-3 mm deep. Pockets that are deeper than 4 mm indicate periodontitis.
- Take dental X-rays to look for bone loss in areas with deep pockets.
Once your dentist has confirmed periodontitis, you may be prescribed some treatments and asked to make lifestyle changes.
How To Treat Periodontitis
Treatments are usually performed by a dentist, a periodontist, or dental hygienist. The main goal of the treatment is usually to clean the pockets around the teeth thoroughly and prevent damage to the surrounding bones and tissues.
You need to follow a good oral care routine and quit tobacco use to get best results from the treatment.
Periodontitis that is not advanced may only require less invasive or non-surgical medical interventions like (6):
- Scaling to remove tartar and bacteria from the surface of your teeth as well as under your gums. This is often done using a laser, an ultrasonic device, or instruments.
- Root planing to smooth down the root surfaces to prevent bacteria and tartar from building up any further.
- Antibiotics – Topical as well as oral antibiotics can help control bacterial infections.
Advanced cases of periodontitis may require surgical interventions like (6):
- Flap Or Pocket-Reduction Surgery – Tiny incisions are made in your gum so that a section of your gum can be easily lifted for more effective scaling and root planing.
- Soft Tissue Grafts – These help reinforce damaged soft tissue. This procedure is often carried out by taking a small amount of tissue from your palate. This graft may also be taken from another donor source.
- Bone Grafting – This is done to reinforce the destroyed bones surrounding the root of your teeth. The graft may be made up of fragments of your own bone or that of a donor. These grafts may also be synthetic.
- Guided Tissue Regeneration – A biocompatible fabric is placed between an existing bone and your tooth to allow the regrowth of the bones that are destroyed by bacteria. This procedure prevents unwanted tissues from entering the healing area.
- Tissue-Stimulating Proteins – This involves the application of a special gel to the diseased tooth root to stimulate the growth of healthy bones and tissues.
Depending on the intensity of damage to your teeth, your doctor may prescribe any of the above treatments to speed up your healing.
It is also recommended that you follow these tips to help the ongoing medical treatments work better.
How To Prevent Periodontitis
- Brush your teeth at least twice daily.
- Floss daily.
- Use a soft toothbrush to brush your teeth and replace it every 3-4 months.
- Use an electric toothbrush if you can as it does a better job in removing plaque and tartar.
- Use a mouth rinse to help reduce the plaque between your teeth and gums.
- Quit smoking or chewing tobacco.
- Get your teeth checked regularly by a dental professional.
It is best to get regular dental check-ups done to detect periodontitis at an early stage so that the damage to your teeth and gums can be easily reversed. If left untreated, periodontitis can lead to complications.
Complications
The following are the complications of periodontitis:
- Tooth loss
- Recurrent gum abscesses
- Increase in damage to the periodontal ligament that connects the tooth to the socket
- Damage to the alveolar or jaw bone
- Loss of teeth
- Receding gums
- Loosening of teeth
Don’t take your oral health for granted. Following a good oral hygiene routine and getting regular dental check-ups done can go a long way in combating as well as preventing periodontitis successfully.
Did you find this post helpful? Tell us in the comments section below.