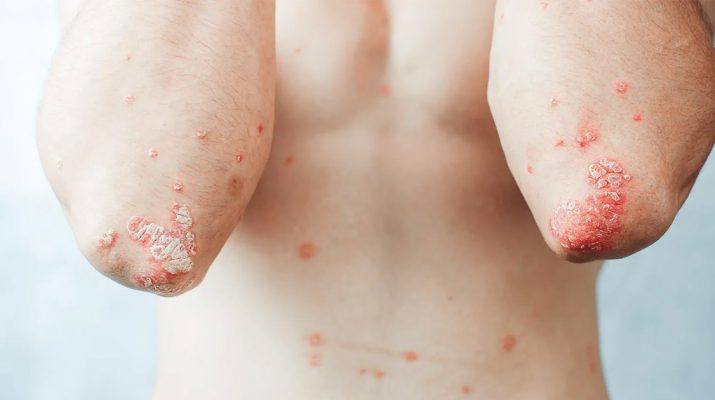
There are no fewer than 80 types of autoimmune disorders. While the name by which they are known may vary, the symptoms of an autoimmune disorder (or disease) remain relatively constant. These include:
- Chest pain
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Hair loss
- Mouth ulcers
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Swollen and painful joints
- Red rashes on the body and face
As the name implies, autoimmune diseases compromise the immune system, causing it to damage the affected area(s). The body’s ability to protect itself from infection is compromised. As a result, immune system cells attach to various areas of the body such as the joints, tissues, nerves, organs, and glands, damaging the area(s).
Common autoimmune diseases include lupus, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis. Inflammatory bowel disease, Graves’ disease, celiac disease, and diabetes type 1 also classify as autoimmune diseases. In the United States, an estimated 24 million people (7% of the U.S. population) suffer from an autoimmune disorder. The disease begins during adulthood, and women are more likely to be diagnosed with the disorder than men.
Diet And Autoimmune Disorder (Ad)
A heightened inflammatory response is a common symptom of an autoimmune disorder. The overproduction of cytokines causes the inflammation of body tissue. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) provides an example of this effect. Excess cytokines in the joints cause pain and inflammation.
Thus, dietary management is an important aspect of treating ADs. Of course, you also want to know which foods to avoid. With this in mind, let’s get to the main point of this article.
Here Are Eight Foods To Never Eat If You Have An Autoimmune Disorder:
Fried Food:
Although we know that the crunchy batter that makes up the top layer of fried food is unhealthy, the high temperature is what stokes the inflammation response. Fried foods are cooked at between 350 to 375 degrees. This produces a neurotoxic chemical called acrylamide to form along with the batter. According to a study published in the journal Toxicology Letters, the neurotoxin causes oxidative stress (which causes cellular damage) via the inflammatory response.
Refined Carbohydrates:
White flour products, otherwise known as “refined carbohydrates,” break down quickly during digestion and cause a spike in blood sugar. A sudden rise in blood sugar stimulates an aggressive inflammatory response. This often causes the symptoms of swelling, joint pain, and muscles aches common in autoimmune diseases.
Trans Fats:
You can often find trans fats in cookies, crackers, donuts, processed snack foods, fried foods, and fast foods. (Look for the words “partially hydrogenated” in the label.) Numerous studies have linked trans fats and systematic, prolonged inflammation.
Alcohol:
While a drink or two may be healthy, scientists state that heavy consumption of alcohol causes systematic inflammation. Moreover, per a study published in the World Journal of Gastroenterology, “chronic inflammation is often associated with alcohol-related medical conditions.” Alcohol is believed to cause inflammation via interactions with bacteria (“microflora”) in the gut.
Vegetable Oils:
The polyunsaturated fatty acid structure of vegetable oils promote oxidative cell damage. Furthermore, vegetable oil, due to high levels of omega-6 fatty acid content, promotes an exacerbated inflammatory response. Vegetable oils include corn, canola (rapeseed), peanut, safflower, sesame, sunflower, and soybean oils.
Processed Meat:
Processed meat includes all meat cooked at a high temperature, including bacon, beef jerky, ham, smoked meat, and sausage. All processed meat contains high levels of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and other inflammatory compounds. Evidence suggests that AGEs link to the development of Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes, heart disease, and kidney failure.
MSG:
In a study published in the Journal of Autoimmunity, Japanese researchers discovered that mice who had been injected with monosodium glutamate (MSG) developed lesions of the liver. Worse, the research suggests that the conditions produced by the MSG-treated mice are similar to two known disease pathways in humans: nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The findings were serious enough for the scientists to recommend a potential elimination of MSG from the food chain.
Aspartame:
Aspartame is an artificial sweetener found in beverages, medications, and food (though it is mostly associated with diet soda.) Despite gaining approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1981, researchers have questioned its safety. After examining research papers published over a 16-year period (2000-2016), a study published in the journal Nutrition Reviews cites numerous potential side effects of aspartame. These include cellular damage, impaired cellular function, and systematic inflammation. Some research claims that aspartame may qualify as a neurotoxin.
Bonus: 5 Foods That Help Inflammation
Per the latest scientific research, here are five of the best foods for fighting inflammation and reducing this symptom of an autoimmune disorder!
Broccoli: Broccoli contains the potent antioxidant glutathione, which serves as a potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant.
Curcumin: The active ingredient in turmeric, curcumin, is a favorite of the Arthritis Foundation. The organization cites the active suppression of arthritis symptoms, including inflammation, and joint pain and stiffness.
Flaxseed: Omega-3s have powerful immune system regulation properties. Flaxseed provides one of the best sources of this fatty acid.
Green tea: Preliminary research suggests that the high concentration of the compound EGCG in green tea may help prevent – and even potentially help treat – autoimmune disorders.
Halibut: Just one regular serving of halibut contains an entire day’s worth of vitamin D, which can help with lupus, multiple sclerosis, and rheumatoid arthritis.